SCC (STRESS CORROSION CRACKING)
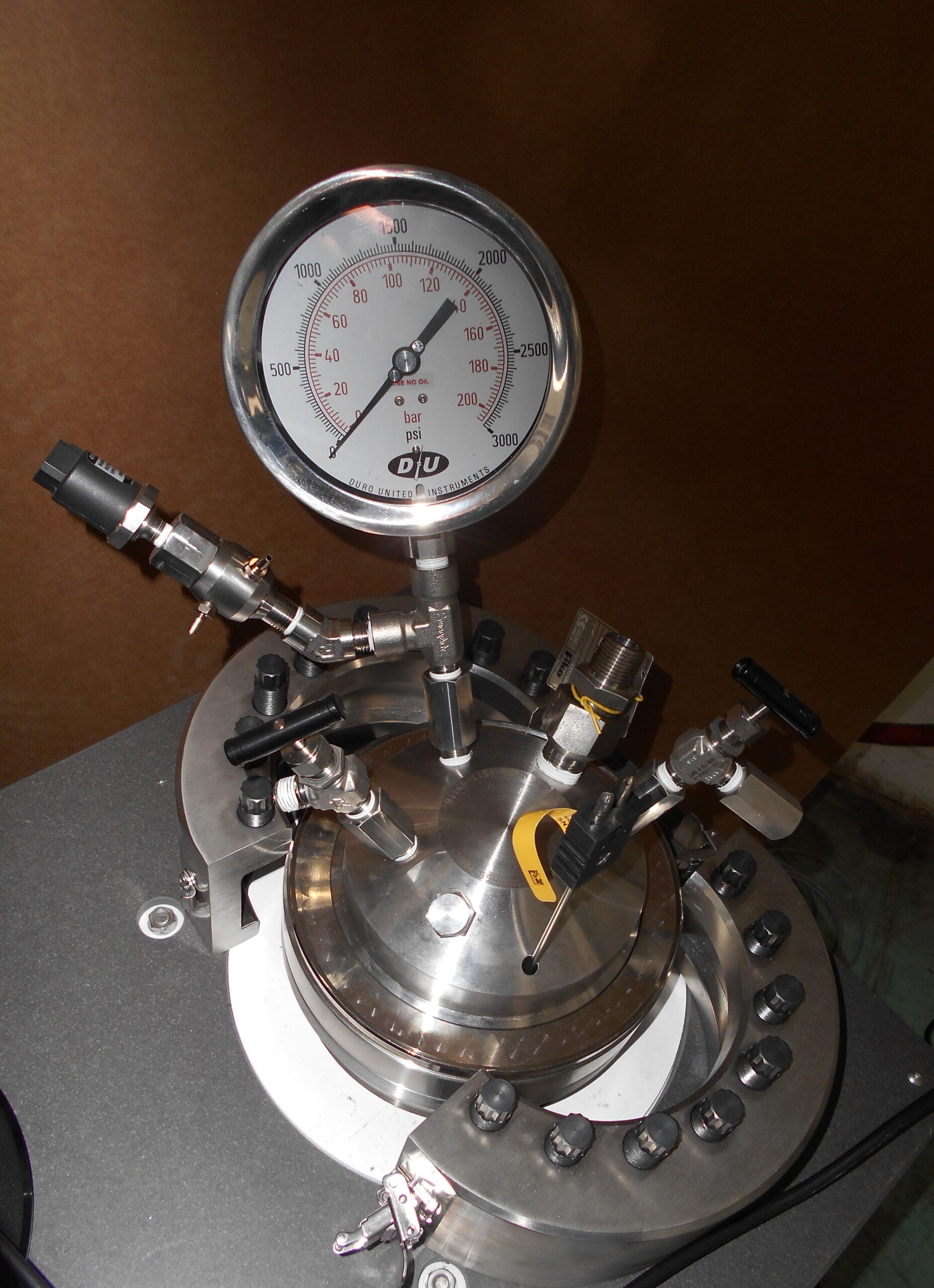
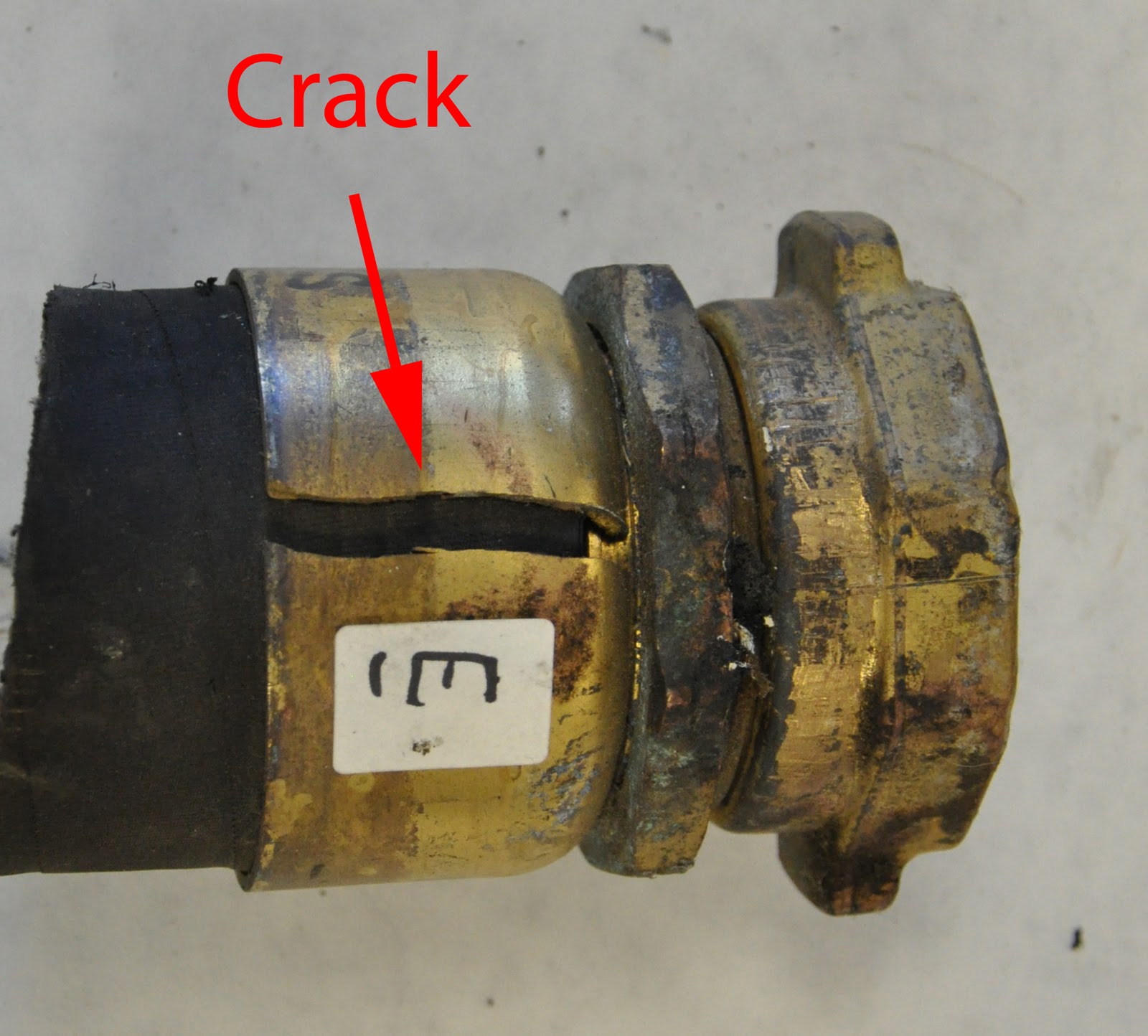
The SCC (Stress Corrosion Cracking) test is meant to evaluate the susceptibility of metallic materials to cracking failure under the combined action of tensile strenght and corrosion in solutions containing hydrogen sulfide (H2S) at high temperatures. This test is commonly carried out according to NACE TM0177 standard and requires a vessel rated to withstand corrosion and equipped with instruments to measure the temperature and pressure of the acid solution, a condenser and other accessories.
TEST METHODS
(20÷300°C; 0÷140 bar)
- ANSI/NACE TM0177 Metodo A + ASTM G49 ANSI/NACE TM0177 Metodo B + ASTM G39
- ANSI/NACE TM0177 Metodo B + EFC 16 3° Edizione + NACE TM0316
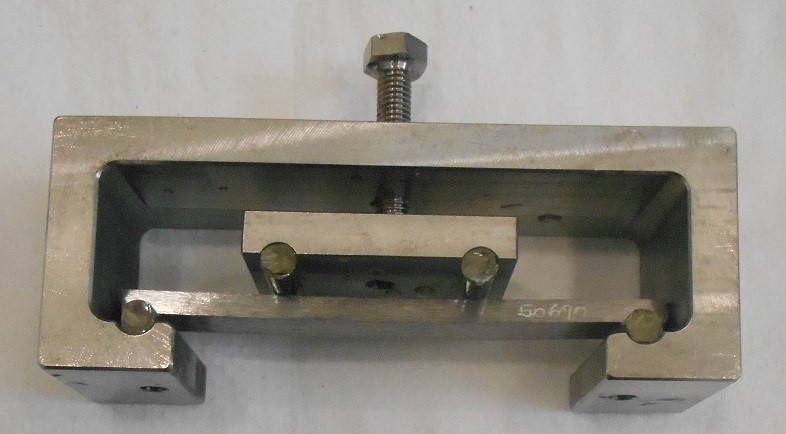
- NACE TM0316 4-point SCC
- ANSI/NACE TM0177 Metodo B 3-point SCC
- ANSI/NACE TM0177 Metodo C C-ring
PHENOMENON DESCRIPTION
Stress Corrosion Cracking phenomenon involves oilfield environment, that requires high-strenght materials in severe service conditions, as sour environments and elevated temperature.
It is a common practice to refer to the phenomenon described above as “Sulfide Stress Corrosion”, but this definition is correct only if tensile stress and corrosion operate at room temperature; it is important to note that the dominant cracking mechanisms for most materials in the presence of H2S vary with temperature.
MORE INFORMATION
Ask a question or request a quote fulfilling the mask below
or call us at (+39) 0523 881 900
Required fields marked with *
YOU NEED ANOTHER TEST?
SIDERTEST
is ACCREDITED FOR A WIDE RANGE OF TESTS